The adjective
An adjective is a word which tell you more about a noun.
Types of adjective
 Since proper adjectives are adjectives derived from proper nouns, there are hundreds, or even thousands of them.
Since proper adjectives are adjectives derived from proper nouns, there are hundreds, or even thousands of them.
Our children are intelligent. (Plural)
Types of adjective
- Adjective of quality
- Adjective of quantity
- Proper adjective
- Adjective of number
- Demonstrative adjective
- Interrogative adjective
- Distributive adjective
- Possessive adjective
The adjectives that are used to describe the nature of a subject or a noun or showing the kind or quality of nouns or pronouns are called Adjective of Quality.
For Example: Kind, Bulky, Weak etc. Adjectives formed from proper nouns are also called adjectives of quality
Adjective of quantity
We can define adjective of quantity as “Adjective of quantity indicates the amount or estimated amount of the noun or pronoun in the sentence. ... “Adjective which shows the quantity of nouns or pronouns is called as Adjective of Quantity”
Examples:-
- He is so
- He has many
- She is very poor
- He has enough money to start business.
- Employees have completed most of the tasks.
Proper adjective
What does proper adjective mean? A proper adjective is a type of adjective. Proper adjective is a word that modifies nouns and pronouns and is formed from a proper noun.
A proper noun is the specific name used for any person, place, or thing.
Proper adjectives typically look like their original proper nouns but have some sort of alternative ending in order to make them adjectives.
Proper Adjective Examples:
- proper noun: America
- I live in America.
- proper adjective: American
- The Fourth of July is an American holiday.
- proper noun: Italy
- I was born in Italy.
- proper adjective: Italian
- I love Italian food.
Proper Adjectives List
 Since proper adjectives are adjectives derived from proper nouns, there are hundreds, or even thousands of them.
Since proper adjectives are adjectives derived from proper nouns, there are hundreds, or even thousands of them.
Some common ones would be anything derived from a country or people group.
- American
- German
- Italian
- French
- Spanish
- Mexican
- Colombian
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Russian
- Chinese
- Korean
- Japanese
As you can see, there are far too many proper adjectives to include on a single list.
Adjective of number
Adjectives are one of the eight parts of speech in the English language. Adjectives are words that modify, or describe, nouns or pronouns. Adjectives tell us which one, what kind, or how many.
Examples of Adjective of Number
red, happy, late, great, foolish, loose, small
Adjectives can be divided into two broad categories: quantity and quality.
An adjective of number is an adjective that tells exactly how many or how much of something there is. It differs from an adjective of quantity that that references a quantity of something that cannot be counted (i.e. some milk, all lemonade). Adjectives of number refer to things that can be counted-even if it is an indefinite amount in the sentence.
Definite Adjectives of Number
These are numbers and amounts, both cardinal numbers and ordinal numbers: one, thousand, gallon, first, fifth, etc. These refer to definite amounts of things.
Indefinite Adjectives of Number
These are adjectives that refer to an indefinite amount of something that can be counted: some, all, many, any, few, no, several, etc. These same words can be used as adjectives of quantity when they refer to something that cannot be counted (i.e. milk, time, water). But, they are adjectives of number when they refer to items that can be counted (i.e. some crackers, many chocolates, no people).
Demonstrative adjective
Demonstrative adjectives are adjectives that are used to modify a noun so that we know which specific person, place, or thing is mentioned.
Examples of Demonstrative Adjectives
When you list two items, you can separate them with a conjunction. Remember that a conjunction is a word that joins two words, phrases, or sentences.
When you list more than two items, you separate them as follows:
Put a comma between all items, and put a comma + and before the last item.
Items in a series can be single words or phrases. In addition, items in a series can be short sentences joined with commas and and.
Examples of items in a series:
Bread, milk, and cheese
Jennifer, Mary, and Charlotte
Red, yellow, and blue
Example of sentences containing items in a series:
1) For breakfast, I had cereal, juice, and toast.
2) My best friends are Paul, Amanda, and Quinn.
3) The moon, the stars, and the sun all appear in the sky.
4) Brush your teeth, wash your face, and go to bed.
5) Christmas trees, cozy sweaters, and warm hot chocolate are three of my favorite things about December.
6) We read books, played games, and went outside to swing.
7) For homework, I have to read this book, do 30 math problems, and make a collage.
8) Spaghetti, pizza, and hotdogs are my brother's favorite foods.
9) On the table, I saw a pair of scissors, tape, a ruler, and some paper.
10) Mrs. Smith, Mr. Thomas, Mrs. Peterson, and Mr. Lance are the four teachers on this hallway.
Remember that a pronoun replaces a noun, so the demonstrative pronouns are used to replace something very specific in context.
Be careful! The demonstrative pronouns can also be used as demonstrative adjectives. When used as an adjective, they come just before a noun to express which one. The function of a pronoun is to replace a noun. So, if you see one of these words in front of a noun, it is most likely acting as an adjective and not a pronoun.
List of demonstrative pronouns:
This (singular)
That (singular)
These (plural)
Those (plural)
Examples of demonstrative pronouns used in a sentence:
1) This is very yummy!
2) I would like those, please.
3) I am not sure that is how you do it.
4) These are the most comfortable.
5) Could you hand me that?
6) This is crazy!
7) Those belong to Sarah.
8) Could you help me move these?
9) That is not mine.
10) Bring me those.
Be careful! The demonstrative adjectives can also be used as demonstrative pronouns. If you see one of these words alone-not preceding a noun or pronoun-it is probably serving as a demonstrative pronoun. Remember that the function of an adjective is to modify a noun or pronoun, so a demonstrative adjective will come just before a noun or pronoun and will tell us which one specifically.
List of demonstrative adjectives:
This (modifies singular nouns/pronouns)
That (modifies singular nouns/pronouns)
Those (modifies plural nouns/pronouns)
Examples of demonstrative adjectives used in a sentence:
1) Those pants are not very comfortable.
2) Do you like this soup?
3) That dress looks good on you.
4) These puppies are very playful.
5) I did not enjoy that book.
6) Did you grow those vegetables in your garden?
7) Can you help me move this box?
8) Mom, can we buy these magazines?
9) This tie is too tight.
10) I like this coat better than that
Distributive adjective
Distributive adjectives are normally used with singular nouns. They include “each”, “every”, “either”, and “neither” and are used to refer to members of a group as individuals.
Distributive Adjectives. Thus, They are: Each, every, neither, either, any, one, both, etc.
- Each: Each is used to refer to one specific person of a group or to speak about group members individually.
For example:
- Each girl will get a chocolate.
- Drink water after each meal.
- Each of my friend went to different collages.
- Each of them are very intelligent.
2. Every: Every is used to make generalization in sentence. It is considered for each and every person in a group.
For example:
- He used to call me every day.
- She watches TV every day.
- I write articles every day.
- She combs her hair every day.
3. Neither: It is used to state not one or the other between a choice of two.
For example:
- I like neither of you.
- Neither of you are allowed in this class.
- I could neither laugh nor cry.
- Neither of us can dance tonight.
4. Either: Either is used to select one person or thing among the choice of two.
For example:
- I can’t do it either.
- Either you do this or I’ll be doing it.
- He doesn’t understand me either.
- I don’t trust him either.
5. Any: It is used to refer to one or some things out of any number of choices. It is also used when the choice is irrelevant.
For Example:
- I don’t want your any advice.
- Do you have any money?
- Any one of you can participate in the competition.
- Is there any money left?
Hence, These are some of the sentences which can help you in framing sentences of Distributive Adjectives.
Interrogative adjective
Adjectives are words that modify, or describe, people, places, things, or ideas. In other words, adjectives modify nouns. Adjectives answer questions like which one, what kind or how many.
Examples of Interrogative Adjectives:
Examples of Adjectives:
Blue sky, wet dog, beautiful sunset
Interrogative adjectives are adjectives that modify nouns when there is a question about which one, what kind, or how many. "Interrogative" means to question. These are common interrogative adjectives: which, what, whose
Examples of Interrogative Adjectives:
which house
what dessert
whose chair
what dessert
whose chair
Be careful. The same words that can function as interrogative adjectives can also function as pronouns. So, you must make sure that the word precedes a noun for it to be an adjective.
Example:
Which cat is yours? (interrogative adjective)
Which is yours? (pronoun)
Which cat is yours? (interrogative adjective)
Which is yours? (pronoun)
Examples of Interrogative Adjectives in Sentences
1. What time will you be arriving for dinner at our house?
2. Which book is your favorite one out of this series?
3. Do you know whose coat this is?
4. Will you tell me which house belongs to the Cook family?
5. Could you help me figure out what cake is grandma's favorite?
6. Which piece of pie would you like to have for dessert?
7. Whose plate was left on the table
2. Which book is your favorite one out of this series?
3. Do you know whose coat this is?
4. Will you tell me which house belongs to the Cook family?
5. Could you help me figure out what cake is grandma's favorite?
6. Which piece of pie would you like to have for dessert?
7. Whose plate was left on the table
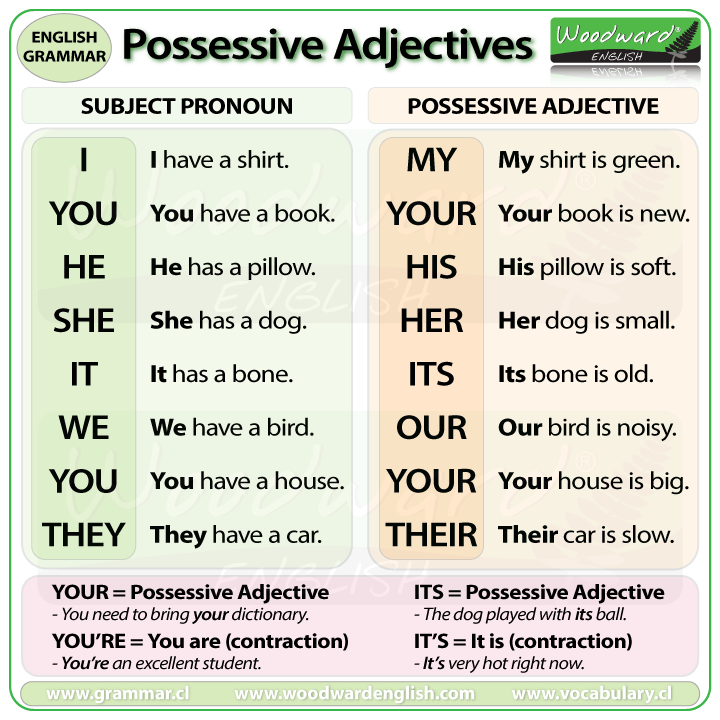
Possessive adjective
Possessive adjectives are used to show possession or ownership of something. While we use them when we refer to people, it is more in the sense of relationship than ownership.
The possessive adjectives in English are as follows:

The possessive adjective needs to agree with the possessor and not with the thing that is possessed.
Examples
- My car is very old.
- Her boyfriend is very friendly.
- Our dog is black.
- Their homework is on the table.
Like all adjectives in English, they are always located directly in front of the noun they refer to. (Possessive Adjective + Noun)
We do not include an S to the adjective when the noun is plural like in many other languages.
Examples:
- Our cars are expensive. (Correct)
Ours cars are expensive. (Incorrect)
However, the verb that is used needs to be in agreement with the noun - if the noun is singular then the verb is singular; if the noun is plural then the verb is plural.
Examples:
- My pen is black. (Singular)
My pens are black. (Plural)
Our children are intelligent. (Plural)



Comments
Post a Comment